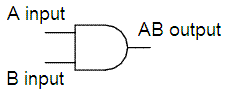
Logical ANDWe're going to examine a couple of examples on boolean operators in Matlab. These operators are useful when we want to develop logic functions in our code. Naturally, we can combine several operations do accomplish very complex functions. Let's start with the basics... A & B performs a logical AND of arrays A and B and returns an array containing elements set to either logical 1 (TRUE) or logical 0 (FALSE).
An element of the output array is set to 1 if both input arrays contain a non-zero element at that same array location. Otherwise, that element is set to 0. A and B must have the same dimensions unless one is a scalar. Example 1: If matrix A is: A = 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 and matrix B is: B = 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 Then, the AND operation between A and B is: >> A & B ans = 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 >> Example 2: If vector x is: x = 0 1 2 3 0 and vector y is: y = 1 2 3 0 0 Then, the AND operation between x and y is: >> x & y ans = 0 1 1 0 0 Boolean AND and other operators From 'Logical AND' to home From 'Logical AND' to 'Boolean Algebra'
|
||||||||