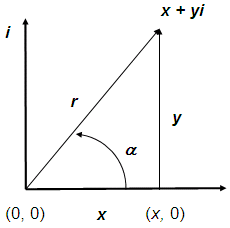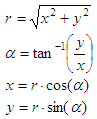Coordinate
conversion: polar-to-
cartesian and cartesian-to-polar
|
This couple of Matlab functions perform a coordinate conversion
of a point given in Cartesian
coordinates to polar
coordinates, and vice versa.
When we use this polar-to-cartesian function, we enter a magnitude and an angle in degrees as
parameters. The function returns a real number (x) and a complex number
(y value).
|
When we use the cartesian-to-polar
function, we enter a
complex value
as parameter. The function returns a magnitude, an angle in
radians and an equivalent angle in degrees.
The formulas for the
conversions are:
where:
x
= abscissa
y = ordinate
r = magnitude
a = angle
These
are
the functions:
function [x,y]=
polar2cart (mag, ang_in_deg)
x = mag
* cos(ang_in_deg*pi/180);
y = j *
mag * sin(ang_in_deg*pi/180);
function [r, ar,
ad] = cart2polar(x)
r =
abs(x);
ar =
angle(x);
ad =
ar*180/pi;
And
now we
test them:
%
Clear memory and screen. Avoid double-blank lines
clear;
clc; format compact
[x, y] =
polar2cart(2, 30.5)
[r, ar,
ad] = cart2polar(7 + 18i)
[r, ar,
ad] = cart2polar(0 - 46.8i)
The
results
are:
x
= 1.7233
y = 0 + 1.0151i
r = 19.3132
ar = 1.1999
ad = 68.7495
r = 46.8000
ar = -1.5708
ad = -90
From
'Coordinate
Conversion' to home
From
'Coordinate Conversion' to 'Matlab Cookbook I'
Table
of Contents
|