Basic MATLAB help
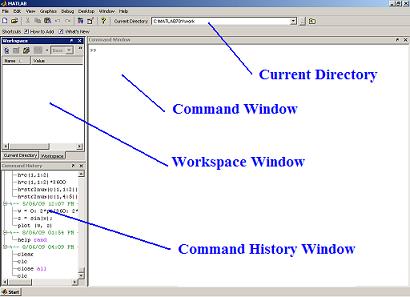 Command window This is the main window. It is characterized by the MATLAB command prompt '>>'. When you launch the application, MATLAB puts you in this window. All commands are typed here, at the MATLAB prompt. Command History All commands typed on the MATLAB prompt in the command window get recorded, even across multiple sessions. You can select a command from this window with the mouse and execute it in the command window by double clicking on it. You can also select a set of commands from this window and create an m-file with the right click of the mouse, and also selecting the appropriate option from the menu. Workspace This subwindow lists all variables that you have generated so far and shows their type and size. You can do various things with these variables by clicking on a variable and then using the right button on the mouse to select your option. Current Directory This is where all your files from the current directory are found. You can do file navigation here. You also have several options of what you can do with a file once you select it. To see the options, click the right button of the mouse after selecting a file. You can run m-files, rename them, delete them, etc. Edit window This is where you write or edit and save your own programs in files called 'M-files'. You can use any text editor to carry out these tasks. MATLAB provides its own built-in editor. However, you can use your own editor by typing the standard file-editing command that you normally use on your system. 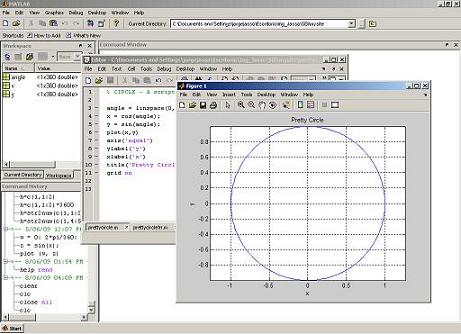 Graphics window The output of all graphics commands typed in the command window is flushed to the Graphics or Figure window, a separate window with white background color. Demo The MATLAB help has a demo facility to show many of its features. The program includes a tutorial introduction that is worth trying. Type 'demo' at the MATLAB prompt to invoke the demonstrations, and follow the instructions. On-line documentation The MATLAB help provides on-line examples for all its built-in functions and programming language commands. You can get Matlab help just typing 'help function' on your command window. You'll see fast-helpful examples. Input-Output MATLAB supports interactive computation, taking the input from the screen, and flushing the output to the screen. Additionally, it can read input files and write output files. Data types The fundamental data type in MATLAB is the array. It includes several distinct data objects: integers, real numbers, matrices, strings, structures, and cells. In most cases you never worry about the data type or object declarations. MATLAB automatically sets its variables to match what you need. Dimensioning Dimensioning is automatic in MATLAB. No dimension statements are required for vectors or arrays. You can find the dimensions of an existing matrix or a vector with the 'size' and 'length' commands. Case sensitivity MATLAB is case-sensitive; that is, it differentiates between the lowercase and uppercase letters. Thus 'm' and 'M' are different variables. MATLAB commands and function are typed in lowercase letters. Output display The output of every command is displayed on the screen unless MATLAB is directed otherwise. A semicolon at the end of a command suppresses the screen output, except for graphics. Output format Computations in MATLAB are performed using double precision, but the appearance of floating point numbers on the screen is controlled by the 'format' in use. There are several different output formats. The following list shows the 'pi' value in several formats:
The formats 'format compact' and 'format loose' control the spacing above and below the displayed lines. The default is format short. Command history MATLAB saves previously typed commands in a buffer. These commands can be recalled with the up-arrow key (this helps in editing previous commands). You can also copy and paste commands from the 'Command History' subwindow where all your commands from even previous sessions of MATLAB are recorded and listed. File types M-files are standard ASCII text files, with a '.m' extension. There are two types of these: script files and function files. Most of the programs that you write in MATLAB are saved as M-files. All built-in functions are M-files, most of which reside on your computer in a special format. Mat-files are binary data-files, with a '.mat' extension to the filename. Matfiles are created by MATLAB when you save data with the 'save' command. The data are written in a special format that only MATLAB can read. These files can be loaded into MATLAB with the 'load' command. Mex-files are MATLAB-callable Fortran and C programs, with a '.mex' extension to the filename. Creating a directory and saving files In MATLAB, there's a default folder called 'work' where MATLAB saves your files if you do not specify any other location. However, it is better if you create a separate folder for saving your work. If you need to store your files somewhere else, you might have to specify the path to the files using the 'path' command, or change the working directory of MATLAB to the desired directory with the 'cd' command. Printing On PCs, you can print the contents of your current active window (command, figure, or edit window), select Print... from the File menu and click Print in the dialog box. File Navigation Starting with MATLAB 6, Mathworks (the MATLAB creators) incorporated new features to easily navigate through your files. The 'Current Directory' is shown just above the Command Window with the option of changing the current directory with just a click. In addition, there is a 'Current Directory' subwindow to the left of the Command Window that lists files in the current directory (you can show/hide it from the 'Desktop menu'), and gives you the option of opening, executing, editing, etc., with the click of the right button on your mouse. You can also change the directory there or add a particular directory to the MATLAB path so that it can access all the files in that directory automatically. From 'Matlab Help' to home From 'Matlab Help' to 'Help Menu'
|